WELCOME TO ASUI
Welcome!
We are accepting new patients
Welcome back!
Click below to login
Learn About Conditions We Treat
ASUI is a community leader in comprehensive urological care, for both men and women, providing service in three East Valley locations. Our urological providers and extensive support staff are dedicated to meeting the needs of all our patients and the community for high quality medical and surgical urology, during business hours, after hours or weekends.

General Health
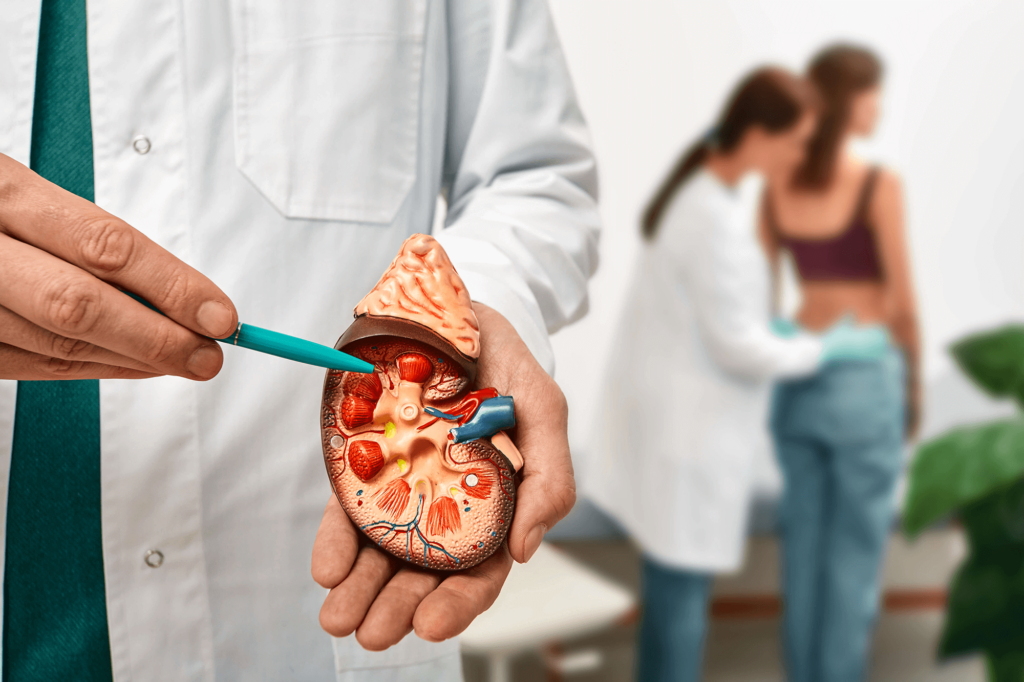
What are Kidney Stones?
A kidney stone is a hard mass of crystals that can form in any part of your urinary tract, including the kidneys, ureters, bladder, or urethra. If urine become too acidic or basic, particles that urine is composed of can clump together to form this crystal. This crystal will grow over time a form a detectable blockage that must be removed for normal urine flow to resume. Sometime crystals are caused by bacterial infection. Kidney stones can be painful to pass, but do not cause any dangerous problems. Mostly, stones can be treated by changing your diet and drinking plenty of water to dilute the particles in your urine that tend to crystalize.
Urinary Tract Infection
UTIs are common and have symptoms like frequent urination urge, pain or burning feeling during urination, foul-smelling urine, and lower abdominal pain. Risk factors include poor hygiene, reduced immunity, sexual activity, and urinary tract abnormalities. Women are more susceptible, but anyone can get them. Antibiotics are used to eliminate bacteria, and it’s important to drink plenty of fluids and manage symptoms. Good hygiene practices, completely emptying the bladder, and using urinary catheters with medical supervision can help prevent UTIs. Untreated UTIs can lead to kidney damage, sepsis, or even death, especially in vulnerable patients.


Hematuria
Blood in the urine, medically referred to as hematuria, can be a cause of concern for many individuals. It is a condition that can be classified into two distinct types, gross hematuria and microscopic hematuria. Gross hematuria refers to the presence of blood in the urine that is visible to the naked eye, while microscopic hematuria is only detected through the use of laboratory testing. It is vital to note that the presence of blood in the urine can be a symptom of several underlying health conditions, some of which could be potentially life-threatening. It is therefore highly recommended to consult with a healthcare provider immediately after blood is observed in the urine. Seeking medical attention can help to determine the cause of the condition, and allow for prompt and effective treatment to be initiated.
Men's Health
Enlarged Prostate (BPH)
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) is a medical condition characterized by the abnormal enlargement of a man’s prostate gland. The prostate gland, which is responsible for the production of sperm, can constrict the urethra or the tube that carries urine from the bladder to the penis, resulting in uncomfortable urinary symptoms. The blockage of the urine’s flow through the urethra is the leading cause of the nagging symptoms attributable to the condition. The symptoms tend to deteriorate over time, and this is primarily because the prostate gland continues to enlarge as time elapses. If you or a loved one experiences these symptoms, it is advisable to seek medical attention as BPH can be effectively managed with the right treatment and care.
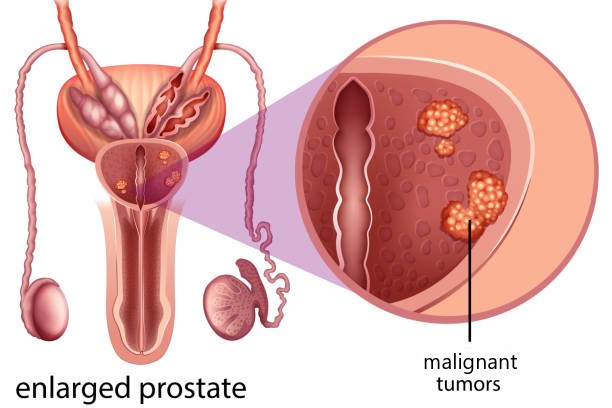
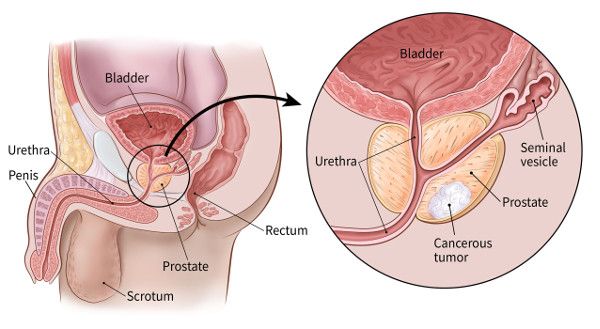
Prostate cancer is a prevalent form of cancer that commonly develops as a gradual cell growth within the prostate gland. Although some forms of the disease may require less intervention due to a slower progression, others can be fast and aggressive, necessitating immediate medical attention. Early detection and diagnosis play a vital role in effectively managing prostate cancer. Healthcare professionals may recommend surgery, radiation therapy, or other specialized treatment options to combat the spread of the disease.
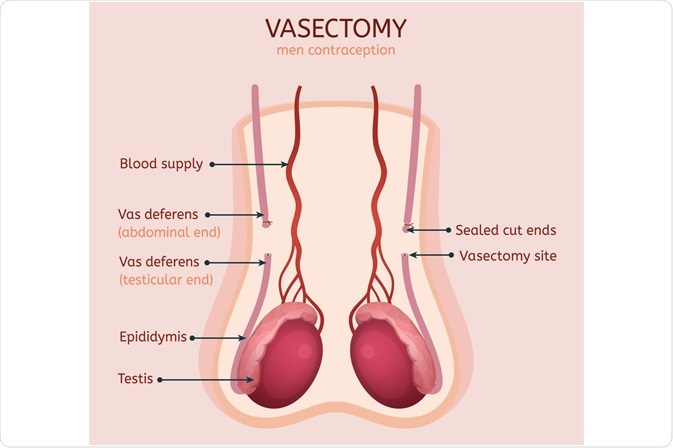
Vasectomy
Approximately 500,000 men opt for a vasectomy every year as a permanent contraceptive measure. Although the procedure can be reversed even several years after the vasectomy, it is noteworthy that the timeframe for reversal is a critical factor in determining the success rate of the procedure and the probability of achieving conception. Furthermore, while a vasectomy is a safe and effective contraception option that guarantees sterility, it does not provide protection from sexually transmitted infections or diseases.
Women's Health

Urinary Incentinance
Urinary incontinence refers to the unintentional loss of bladder control. Among adult women, stress urinary incontinence is the most frequently encountered bladder control challenge, affecting around one in three. Women of any age may experience this problem. Although there are different types of urinary incontinence, women with this issue typically suffer from uncontrolled urine leakage. The amount and frequency of leakage may vary, but dietary adjustments or medical assistance can frequently provide relief.
Overactive Bladder (OAB)
Overactive bladder (OAB) is a medical condition characterized by sudden, frequent, and uncontrollable urges to urinate prior to the bladder filling up completely. This can lead to a number of uncomfortable and inconvenient symptoms such as the frequent need to urinate during the day or night and involuntary leakage of urine. The condition can cause significant disruption to patients’ everyday lives. Individuals with OAB may experience sudden and urgent urges to urinate along with frequent urination which can happen more than 8 times in a 24-hour period.

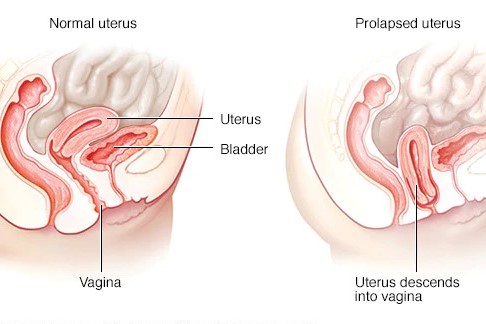
Pelvic Organ Prolapse
Pelvic floor disorders, including prolapse, are a common health concern that affects nearly 24% of women. Prolapse is the medical term used for the slipping down and forward of an organ due to weakened or stretched connective tissue. Such conditions can cause pain during intercourse, incontinence, or a bulging sensation. Prolapse can occur due to weakened muscles or ligaments that support a woman’s pelvic organs. The risk of developing prolapse is higher years after childbirth, post-hysterectomy or during menopause. If you have experienced any of these symptoms, it is essential to seek medical attention to successfully manage them.
